Food processing preserves food, improves safety, and shapes nutrition and daily life.
I have spent years studying food systems and working with producers, so I know why is food processing important how does it affect people at practical and policy levels. This article walks you through clear answers, real-life examples, risks, and smart choices so you can understand how processed foods touch health, budgets, culture, and the environment.

What food processing means
Food processing covers any change to raw food to make it safe, tasty, or longer lasting. It can be simple, like washing and cutting vegetables, or complex, like making canned soups and frozen meals. Processing also includes preservation, packaging, temperature control, and fortification.
Why is food processing important how does it affect people ties into this broad definition. Processing bridges the gap between farm and fork. It turns perishable crops into usable products. It also helps move food from rural farms to city tables in safe form.

Why is food processing important
Food processing is important because it reduces waste, prevents disease, and makes food available year-round. It helps feed more people by making food transportable and storable. It also supports jobs and local economies.
When asking why is food processing important how does it affect people, think of a few clear functions:
- Safety: Processing kills pathogens and reduces spoilage.
- Access: It extends shelf life, so food reaches distant markets.
- Nutrition: It can add vitamins or remove harmful components.
- Convenience: It saves time for busy households.
How food processing affects people: health, safety, and nutrition
Food processing affects people in many direct ways. It can improve public health by reducing foodborne illness. It can also change nutrient content and influence diets.
Health and safety
- Processing kills bacteria and parasites through heat and sterilization.
- Packaging prevents contamination during transport.
- Regulation and testing reduce outbreaks.
Nutrition and diet
- Processing can remove or add nutrients. For example, milling can strip fiber, while fortification adds vitamins.
- Highly processed foods can be high in sugar, salt, and fat and may promote overeating.
- Light processing preserves nutrients while making food safer and easier to eat.
Mental and social effects
- Processed foods influence habits and culture. They shape meals, convenience, and time spent cooking.
- Food marketing and packaging change preferences and expectations.
Why is food processing important how does it affect people? It shapes both what we eat and how healthy our diets are. The net effect depends on the type and frequency of processed foods people consume.
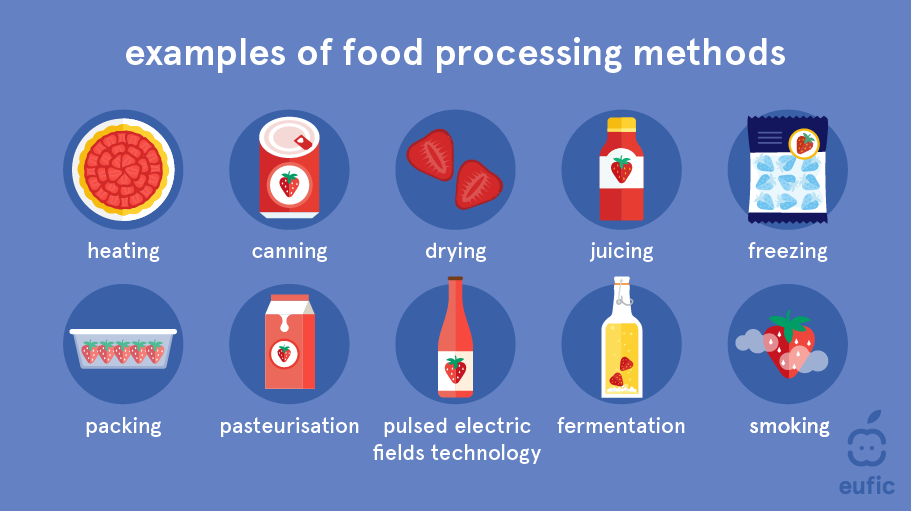
Types and examples of food processing
Food processing spans a wide range. Grouping helps you see benefits and risks.
Common types
- Minimal processing: washing, chopping, pasteurizing.
- Moderate processing: canning, freezing, drying.
- High processing: ready meals, snacks, sweetened beverages.
Examples
- Pasteurized milk reduces bacterial risk and lasts longer.
- Frozen vegetables lock in nutrients for months.
- Packaged snacks often add sugar, salt, and preservatives.
Why is food processing important how does it affect people? The type of processing determines safety, nutrition, and environmental costs. Choose wisely based on needs.

Benefits and risks of food processing
Processing brings big benefits and clear risks. Weigh both to make informed choices.
Benefits
- Less food waste from spoilage.
- Better food safety and fewer infections.
- Consistent quality and year-round supply.
- Fortified foods can prevent nutrient deficiencies.
Risks
- Loss of fiber and some micronutrients in refined products.
- Overconsumption of ultra-processed foods linked to chronic disease.
- Environmental costs: packaging and energy use.
- Economic inequality when healthy processed foods are unaffordable.
Why is food processing important how does it affect people? It can be a public health tool or a contributor to diet-related illness. Policy and personal choice guide the balance.
Practical tips for choosing and using processed foods
You do not need to avoid processed foods to eat well. Use these practical tips.
How to choose smarter
- Read ingredient lists. Short lists often mean less processing.
- Choose minimally processed whole foods when possible.
- Look for fortified staples if you lack dietary variety.
- Watch added sugar, salt, and saturated fat amounts.
How to use processed foods well
- Use canned or frozen produce to lower cost and waste.
- Combine processed proteins with fresh vegetables for balance.
- Cook from ready components to save time and control ingredients.
Why is food processing important how does it affect people? Smart choices let you keep benefits like safety and convenience while limiting harm.
Personal experience and lessons learned
I once audited a small food plant to improve shelf life and quality. The team added simple pasteurization and better packaging. Spoilage dropped by half, and fewer customers reported stomach issues. We also added clear labels and a small fortification step that reduced local micronutrient gaps.
Lessons I learned
- Small processing steps can have big public health benefits.
- Transparency builds trust. Clear labels cut consumer confusion.
- Overprocessing for shelf life can undermine nutrition and taste.
Why is food processing important how does it affect people? My work showed that reasonable processing, paired with good labelling, improves health and trust.

Policy, safety systems, and future trends
Governments and industry shape how processing affects people. Safety rules, standards, and innovation matter.
Policy and regulation
- Food safety laws enforce hygiene, testing, and recalls.
- Fortification programs target common deficiencies.
- Labelling rules help consumers compare products.
Trends to watch
- Cleaner-label processing that uses fewer additives.
- Alternative proteins and novel preservation methods.
- Circular packaging and reduced food waste systems.
Why is food processing important how does it affect people? Policy and innovation can steer processing toward better health and lower environmental impact.
Frequently Asked Questions of why is food processing important how does it affect people
What is the main reason food processing is necessary?
Processing is necessary to make food safe, extend shelf life, and enable transport to distant markets. It reduces spoilage and foodborne illness.
Does processing always reduce nutrition?
Not always. Some processes reduce nutrients, but others preserve or add them. Fortified and frozen foods can be very nutritious.
Are all processed foods unhealthy?
No. Minimal processing like pasteurizing or freezing often improves safety and convenience without harming nutrition. The problem is frequent use of ultra-processed products high in sugar and salt.
How does food processing affect food prices?
Processing can lower costs by reducing waste and enabling scale. It can also add value and price premiums for convenience and branding.
Can food processing help solve hunger?
Yes. Processing helps stabilize supplies, preserve seasonal bounty, and fortify staples, which can reduce hunger and nutrient deficiencies.
Conclusion
Food processing is a powerful tool. It keeps food safe, reduces waste, and makes modern diets possible while also shaping nutrition, culture, and the environment. By understanding why is food processing important how does it affect people, you can make better choices, support sound policies, and use processed foods in ways that protect health and reduce harm. Take small steps: choose minimally processed options, read labels, and support transparent food systems. Share your experiences, ask questions, or subscribe for deeper guides on choosing and preparing processed foods.